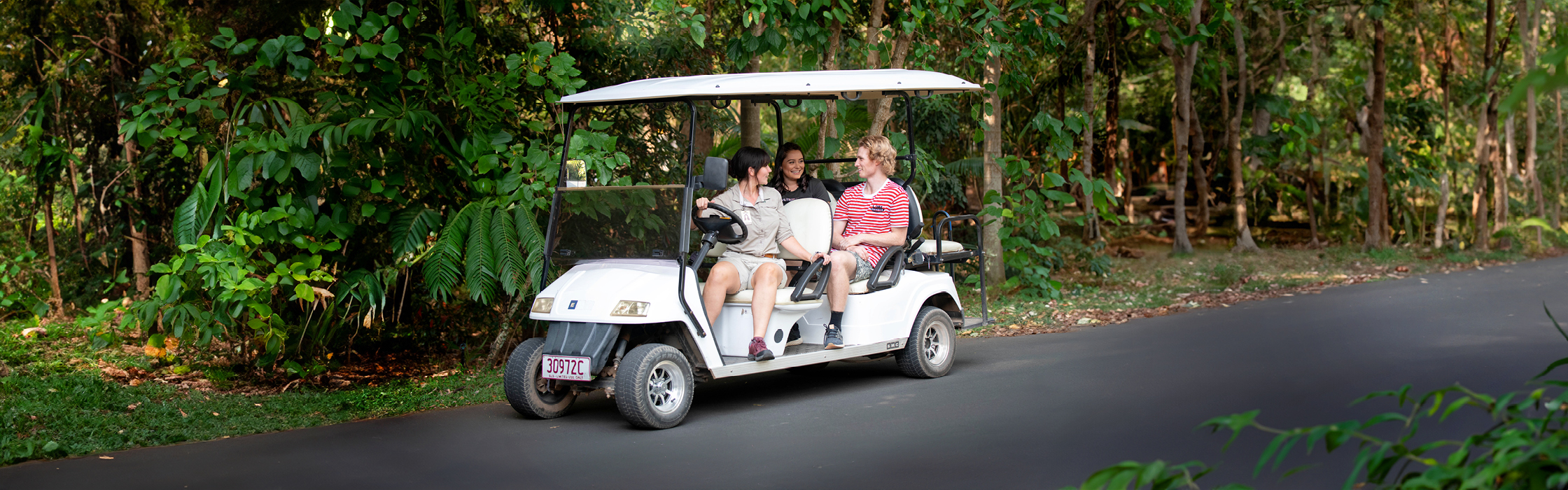
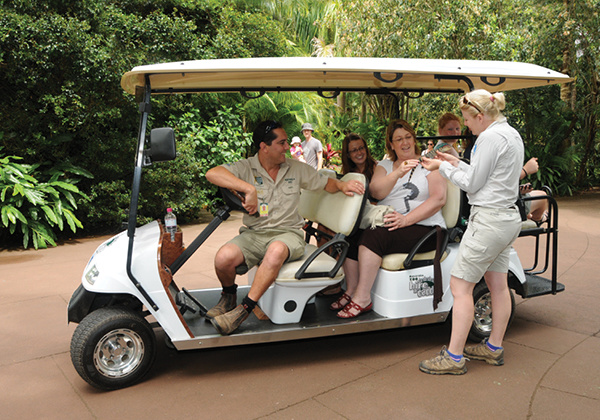
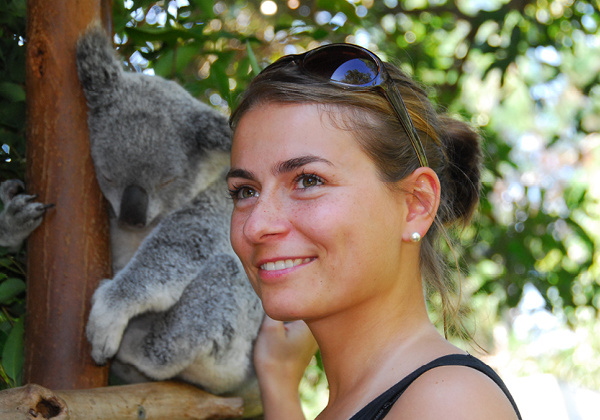
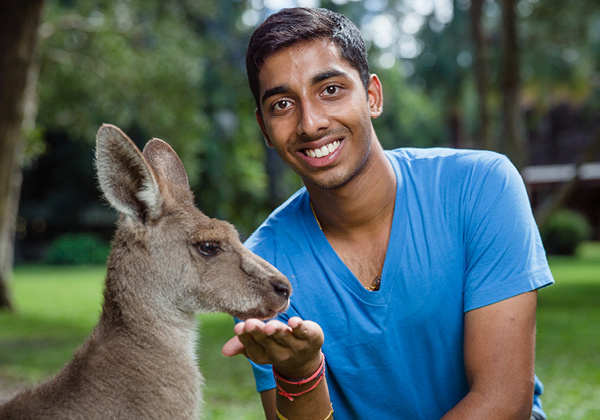
Hire a Caddie Tour
Cost: $599
Tour duration: Five hours
No. of people: Maximum 5*
Explore Australia Zoo in style with 5-star service onboard the Hire a Caddie Tour! Our passionate and knowledgeable tour guides will be your chauffeur, taking you on a customised journey around our world-class, 110-acre facility.
Be prepared for an action-packed day of animal interactions including feeding our kangaroos. Experience all of the jaw-snapping, death-rolling action in the Wildlife Warriors show, from your reserved seating in our world-famous Crocoseum.
You will learn all about our gorgeous animals, the history of Steve Irwin and his vision for Australia Zoo, as well as our international conservation efforts and amazing wildlife hospital. This tour is the perfect way to explore the Zoo at your own pace. All you have to do is sit back and relax as our wonderful tour guides take you on an unforgettable journey!
* For groups of more than 5 people, please contact our Tour Desk on 07 5436 2002 or email guestservices@australiazoo.com.au.
Additional Information
- Zoo entry is required
- Children under 15 years must be accompanied by a paying adult
- Animal encounters can be booked upon request, additional fees apply
- Crikey Cafe lunch can be preordered upon arrival, additional fees apply
- Tour runs for five hours – five hours include any shows, lunch and animal encounters taken during the tour